This documentation is related to an older version of Firebolt. For the most current documentation, see Firebolt documentation.
Firebolt architecture overview
The diagram below depicts Firebolt’s high-level architecture, which comprises a services layer and decoupled storage and compute layers. This topic describes each layer.
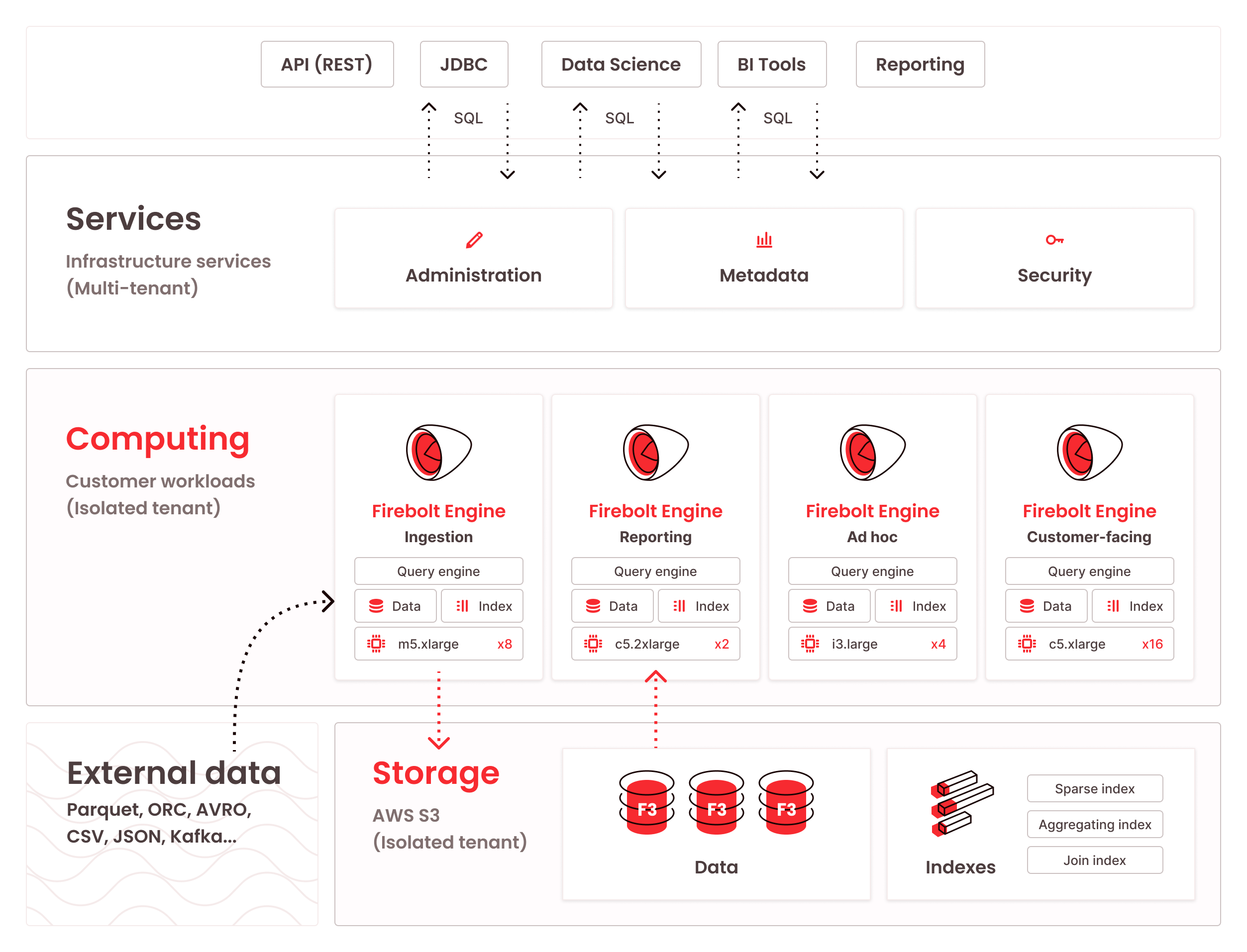
Services Layer
The services layer is multi-tenant. It accepts all incoming requests to Firebolt. Its most important functions are:
- Administration - Handles account information, user management, and permissions.
- Metadata - Contains all metadata of databases, engines, tables, indexes, etc.
- Security - Handles authentication.
Isolated Tenancy
Unlike the multi-tenant services layer, the compute and storage layers in Firebolt run on isolated tenants. A dedicated and isolated AWS sub-account is created for each Firebolt customer, within which Firebolt manages the storage and compute layers. Each tenant runs within Firebolt’s master account and outside their own VPC. This ensures complete cross-customer isolation for data and query execution.
Compute Layer
The compute layer runs Firebolt engines. Engines are compute clusters that run database workloads. Each engine is an isolated cluster. Within each cluster, engine nodes store data and indexes in the local cache. The engine loads data from the storage layer into cache at query runtime based on the query configuration.
A benefit of the decoupled storage and compute architecture is that multiple engines can be assigned to the same database. This allows for granular control over which hardware is assigned to which tasks. Each engine can have a different configuration and size depending on the workloads. Engines can work in parallel or separately, and you can share them with different people in your organization.
Storage Layer
The storage layer within Firebolt runs on Amazon S3. After you ingest data into Firebolt, this is where the data and indexes associated with a database are saved. When you ingest data, you use a Firebolt general purpose engine, which stores the data in the proprietary Firebolt File Format (F3). The data is sorted, compressed, and indexed to support highly efficient pruning for query acceleration. F3 works together with other proprietary Firebolt technologies to deliver exceptional performance at query runtime.